Backup from cStor
This website/page will be End-of-life (EOL) after 31 August 2024. We recommend you to visit OpenEBS Documentation for the latest Mayastor documentation (v2.6 and above).
Mayastor is now also referred to as OpenEBS Replicated PV Mayastor.
Step 1: Backup from CStor Cluster
In the current setup, we have a CStor cluster serving as the source, with Cassandra running as a StatefulSet, utilizing CStor volumes.
kubectl get pods -n cassandra NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cassandra-0 1/1 Running 0 6m22s
cassandra-1 1/1 Running 0 4m23s
cassandra-2 1/1 Running 0 2m15skubectl get pvc -n cassandra NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
data-cassandra-0 Bound pvc-05c464de-f273-4d04-b915-600bc434d762 3Gi RWO cstor-csi-disk 6m37s
data-cassandra-1 Bound pvc-a7ac4af9-6cc9-4722-aee1-b8c9e1c1f8c8 3Gi RWO cstor-csi-disk 4m38s
data-cassandra-2 Bound pvc-0980ea22-0b4b-4f02-bc57-81c4089cf55a 3Gi RWO cstor-csi-disk 2m30skubectl get cvc -n openebs NAME CAPACITY STATUS AGE
pvc-05c464de-f273-4d04-b915-600bc434d762 3Gi Bound 6m47s
pvc-0980ea22-0b4b-4f02-bc57-81c4089cf55a 3Gi Bound 2m40s
pvc-a7ac4af9-6cc9-4722-aee1-b8c9e1c1f8c8 3Gi Bound 4m48sStep 2: Velero Installation
To initiate Velero, execute the following command:
velero install --use-node-agent --provider gcp --plugins velero/velero-plugin-for-gcp:v1.6.0 --bucket velero-backup-datacore --secret-file ./credentials-velero --uploader-type resticVerify the Velero namespace for Node Agent and Velero pods:
kubectl get pods -n veleroStep 3: Create a Sample Database
In this example, we create a new database with sample data in Cassandra, a distributed database.
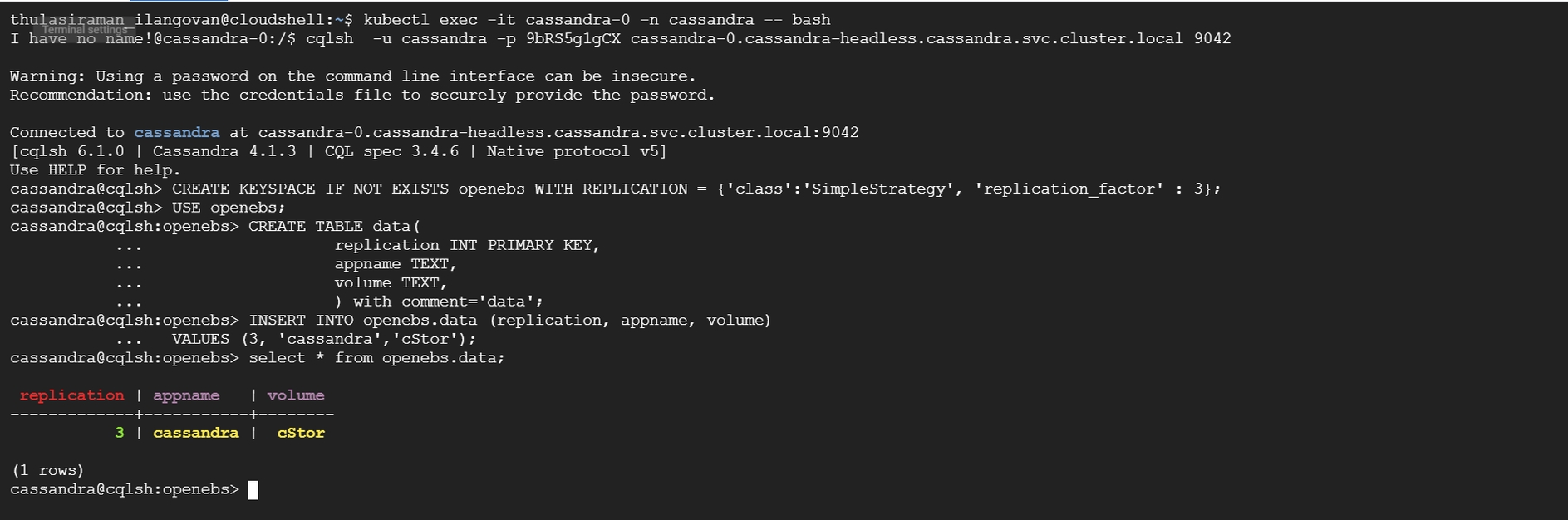
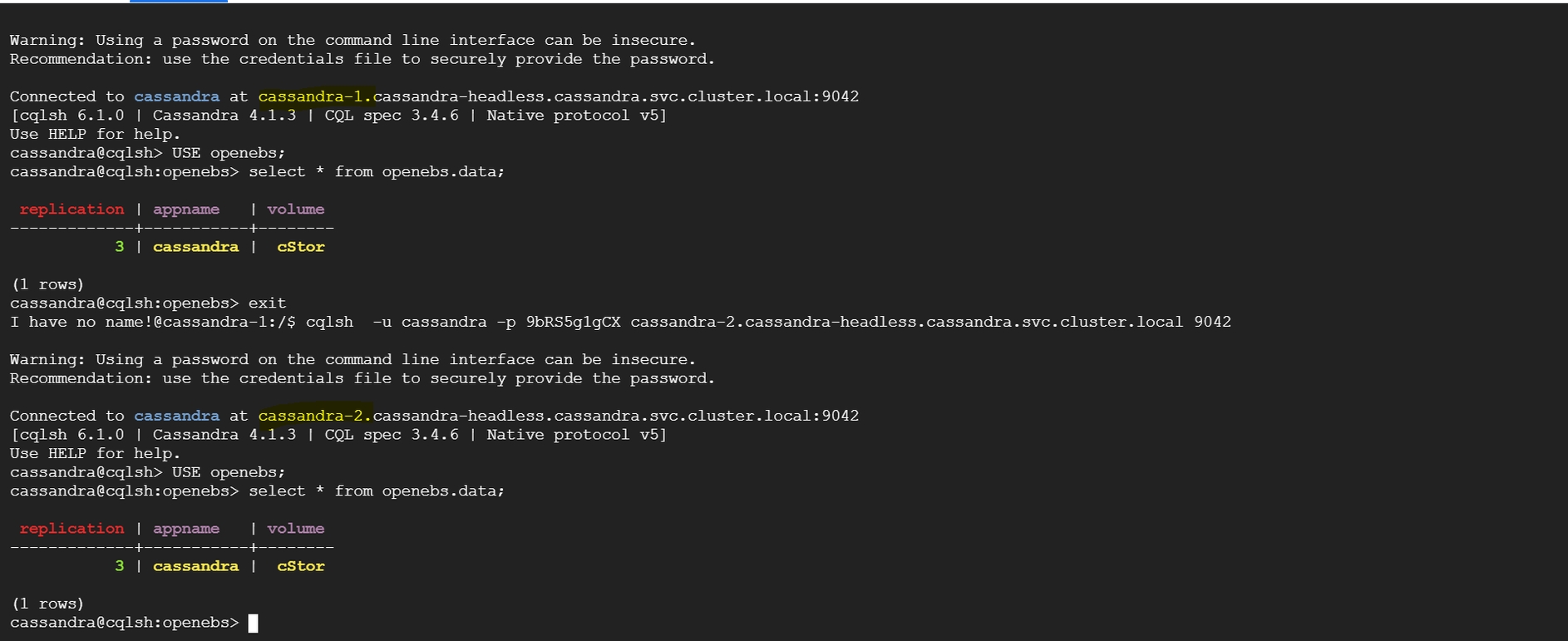
The data is distributed across all replication instances.
Step 4: Taking Velero Backup
Cassandra is a distributed wide-column store database running in clusters called rings. Each node in a Cassandra ring stores some data ranges and replicates others for scaling and fault tolerance. To back up Cassandra, we must back up all three volumes and restore them at the destination.
Velero offers two approaches for discovering pod volumes to back up using File System Backup (FSB):
Opt-in Approach: Annotate every pod containing a volume to be backed up with the volume's name.
Opt-out Approach: Back up all pod volumes using FSB, with the option to exclude specific volumes.
Opt-in:
In this case, we opt-in all Cassandra pods and volumes for backup:
To perform the backup, run the following command:
Check the backup status, run the following command:
Last updated
Was this helpful?